Gyeeta Install Planning and Options
Readers are advised to read the Gyeeta Architecture page before reading this section.
Install Options for Gyeeta components
Gyeeta components can be installed using any of the following methods :
- Bash Script based Installation and Configuration (easiest install option)
- Kubernetes Helm Chart
- Docker Containers
- rpm / deb based native packages for dnf/yum, apt-get or zypper
- Manual Tar Package download and configure
Installing using either the Bash Script or Kubernetes Helm Charts are the easiest ways to deploy the various Gyeeta components.
Host Requirements
CPU Architectures Supported
Gyeeta currently supports only x86_64 processors. Also, only Intel/AMD processors released after 2012 are supported as Gyeeta is
compiled with avx instruction support.
Serverless monitoring not supported
Currently Gyeeta does not support monitoring of Serverless environments such as AWS Lambda and Fargate.
GKE Support
Gyeeta supports Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) - Standard mode only. GKE Autopilot is not supported.
Minimum Linux Kernel Versions
Gyeeta components support only hosts with Linux Kernel 4.4 or higher (Linux 4.4 was released in 2016).
Supported Linux Distributions
| OS Distribution | Supported Versions |
|---|---|
| Ubuntu | 18 & higher |
| Debian | 9 & higher |
| RHEL, CentOS, Rocky Linux, Oracle Linux | 8 & higher |
| Amazon Linux 2023 | All Versions |
| Amazon Linux 1 and 2 | All Versions |
| Google Container OS (COS) | Linux Kernel 4.14 & Higher |
| Fedora | 28 & higher |
| OpenSUSE, SUSE Linux | 15 & higher |
Other Linux distributions based on Debian/Ubuntu or RHEL are supported as long as the base Linux Kernel is 4.4+
Container Platforms such as Kubernetes or Docker Swarm are also supported using Helm Charts or Docker containers.
Planning the Gyeeta Deployment
For smaller environments (with upto 150 hosts to be monitored), users can quickly install all Server components on a single host with at least 4 cores and 8 GB RAM using the TLDR Quick Server Install
To setup Gyeeta, users need to install the following minimal components :
- One or more instances of PostgresDB Servers for both Shyama and Madhava servers
- One instance of Shyama Central Server
- One or more instances of Madhava Intermediate Servers
- On each host to be monitored, a Partha Host Monitor Agent to be installed
- One instance of Node Webserver
- One instance of Alert Action Agent responsible for executing Alert Actions (Notifications)
The image below shows the high level overview of how the different components interact with each other :
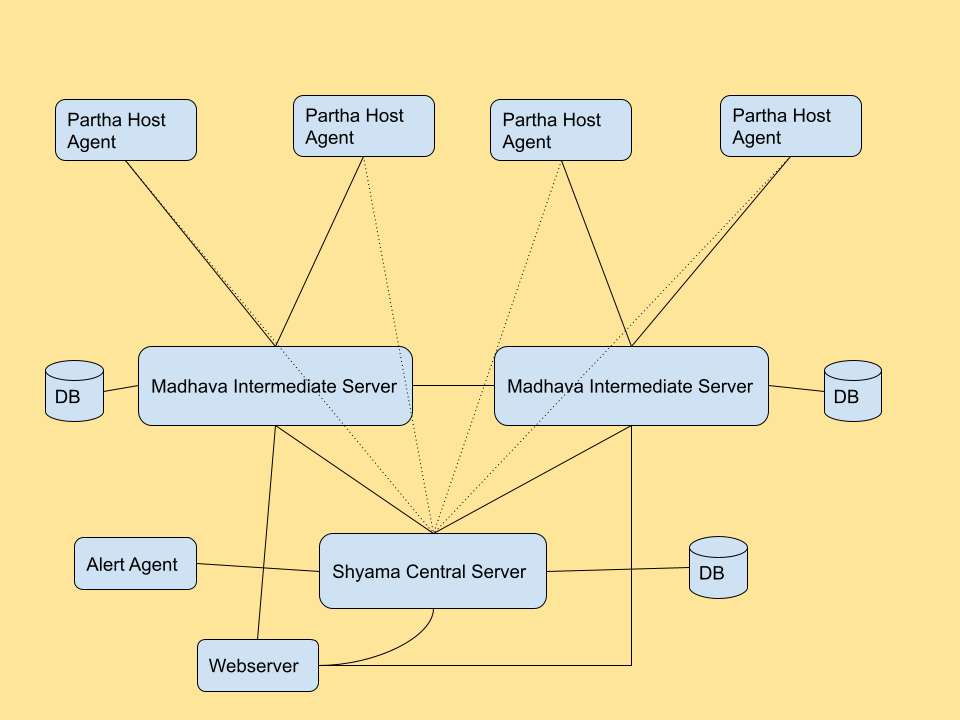
Number of Madhava Servers needed
The number of Madhava Intermediate servers that are needed depends on the max number of monitored hosts and Network Locality of the monitored hosts with the Madhava servers.
The maximum number of monitored hosts a single Madhava server instance can handle depends on the Madhava host CPU and RAM specs and can range from 50 monitored hosts for a small Madhava host with 2 CPU cores and 4 GB RAM to 400 monitored hosts for a server with 16 cores and 32 GB RAM.
Also, it is recommended that the monitored hosts and the Madhava server reside in the same Network Zone for better performance and to reduce Network egress costs.
The Shyama server will assign each monitored host a Madhava server depending on Network Locality and Madhava server availability.
A maximum of 3 Madhava servers can share a single Postgres DB instance. This implies that as the number of Madhava servers increases, the number of Postgres DB instances will also increase.
Multiple Madhava servers can also be installed on a single Host, if needed. This requires the Madhava servers to either installed as Docker containers or using tarball extracts.
Network Connectivity & Firewall Considerations
The Partha Host Agent does not open any TCP port. No incoming connections will be made to any Partha agent. The Partha agent will need to connect externally to the Shyama server and Shyama assigned Madhava servers though.
The Shyama server, the Madhava Intermediate servers and the Node Webserver are all connected to each other in a mesh style network. So in case of multi-region/multi-zone deployments, the Shyama server, the Madhava servers and Node Webserver need to be able to connect to each other.
The Shyama Server needs to be accessable to all the Monitored Hosts as well as to other Gyeeta components (Postgres DB, Madhava, Webserver, Alert Agent).
The Madhava Server needs to be accessable to a subset of the Monitored Hosts (same Network Zone/Region), to the Shyama server, other Madhava server instances, the Postgres DB and Webserver.
The Webserver needs to connect to the Shyama server and all Madhava instances. The Webserver will not connect to any Monitored Hosts.
The Alert Agent needs to connect to the Shyama Server only. If external Alert Actions (Notifications) are setup such as a Slack or Pagerduty Notification, the Alert Agent will need to access the Internet in such cases.
TL;DR Quick Single Command Install
For smaller environments of upto 200 hosts, users can quickly install and try out Gyeeta using the TLDR Quick Server Install.
This will install all Server components (One Postgres DB, One Shyama, one Madhava, Node Webserver) and Alert Agent on a single host using a single command. Users will then need to install additional Partha Agents on all hosts which need to be monitored.
If using the TLDR Quick Install, users can skip all subsequent sections pertaining to Installation of Gyeeta Server components and Alert Agent.
Recommended Install Sequence
The recommended sequence for installing various components include :
- Install and configure one or more Postgres DB server(s).
- Install the Shyama server.
- Install one or more Madhava servers depending on the number of hosts to be monitored.
- Install the Partha Host Agents on each host that needs to be monitored.
- Install the Node Webserver.
- Install the Alert Action Agent.
For information on Kubernetes Helm chart deployment, please refer to Kubernetes Helm Charts link.
Installing the Shyama Postgres DB
The first component that should be installed is the Shyama server's Postgres DB server. The Postgres DB must be installed in the same Network Zone as the Shyama server.
This step can be ignored for Kubernetes Helm chart installs as the Helm chart deploys a Postgres DB container automatically.
More info about the Install Steps, Disk space needed and CPU, Memory requirements can be found at Postgres DB Install link.
Installing the Shyama Central Server
The Shyama Server is the component to which all other Gyeeta components and all monitored hosts will connect to. This implies that the Shyama Central Server needs to be accessible from other components and if other components or monitored hosts are located in different Network Regions/Zones, connectivity to Shyama server is needed (for example, using VPC Network Peering).
More info about the Shyama Central Server Install Steps can be found at Shyama Install link.
Installing one or more Madhava Postgres DBs
The Madhava Postgres DB must be installed in the same Network Zone as the Madhava servers. In case the Madhava server is located in the same Network Zone as the Shyama server, the Shyama Postgres DB can also be used by upto 3 Madhava servers.
This step can be ignored for Kubernetes Helm chart installs as the Helm chart deploys a Postgres DB container automatically.
More info about the Install Steps, Disk space needed and CPU, Memory requirements can be found at Postgres DB Install link.
Installing one or more Madhava Intermediate Servers
The number of the Madhava servers should be decided and accordingly installed.
The Madhava servers need to be able to connect to the Shyama Central Server and other Madhava server instances. Each Partha Host Agent will connect to its Shyama assigned Madhava Server and so monitored hosts need to be able to connect to the Madhava servers.
Also, the Webserver will connect to each Madhava server instance for Query resultsets.
More info about the Madhava Server Install Steps can be found at Madhava Install link.
Installing Partha Host Monitor Agent on all hosts to be monitored
The Partha Host Agent needs to be installed on each of the monitored hosts. The Partha Agent needs to be able to connect to the Shyama Central Server who will then assign the nearest Madhava Intermediate server and then all further communication of the Partha agent will be with the Madhava server.
No incoming connections will be made to any Partha agent.
More info about the Partha Host Agent Install Steps can be found at Partha Install link.
Installing Node Webserver
The Nodejs Webserver needs to be installed on a host which can connect to the Shyama Central Server and all Madhava Intermediate servers.
Users will connect to the Node Webserver for the Web UI and REST API querying.
More info about the Node Webserver Install Steps can be found at Node Webserver Install link.
Installing Alert Action Agent
The Alert Action Agent is responsible for executing the Alert Notifications or Actions and communicates with the Shyama instance as Shyama server also acts as the Alert Managet.
The Alert Action Agent needs to be installed on a host which can connect to the Shyama Central Server. If external Alert Notifications are to be executed (for example, email action, PagerDuty), the Alert Action Agent will need to communicate with those external servers as well.
More info about the Alert Action Agent Install Steps can be found at Alert Action Agent Install link.